
Each water system is unique and has different needs. Please contact our office at 603-868-3212 with specific questions about your well and filtration system.
An overwhelming 85% of the U.S.A. has hard water. The minerals that make up hard water are not considered toxic; that is, they do not cause harmful health effects but water hardness can cause major problems for your home and daily living. Humans had been living with the problems of hard water since the beginning of our relationship with water but it wasn’t until the early 1900’s when the “modern day” water softener was conceived. Water technology has significantly improved since then but the scientific thinking behind it has remained the same.
This article will go over:
- What is a water softener is
- What are the benefits of having a water softener
- How does a water softener remove hardness from the water
- How often should you be adding salt to the brine tank
- Troubleshooting a water softener
What is a water softener?
A water softener uses a cation exchange resin media to remove hardness from your water. The beads are a plastic polymer material, specially formulated to grab on to specific chemical substances. The surface of the resin is pre-charged with salt ions. As hard water passes through the resin, the individual beads will release the salt ions and exchange them for the hardness ions. This process is called an ion exchange.
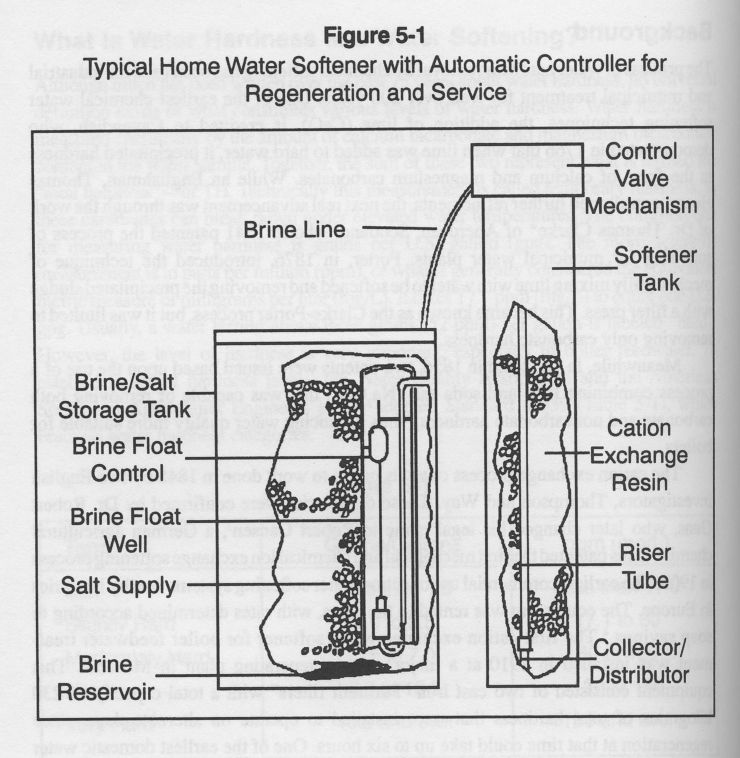
A water softening system features a fiberglass tank that holds the resin beads, a softening valve on top of the fiberglass tank that directs the flow of water, a riser tub with a collector/distributor that is connected to the valve and a brine tank that houses salt/brine solution. The brine solution is used to regenerate the resin beads. A system may also need pretreatment in order to protect the resin bed and ensure its effectiveness in removing water hardness.
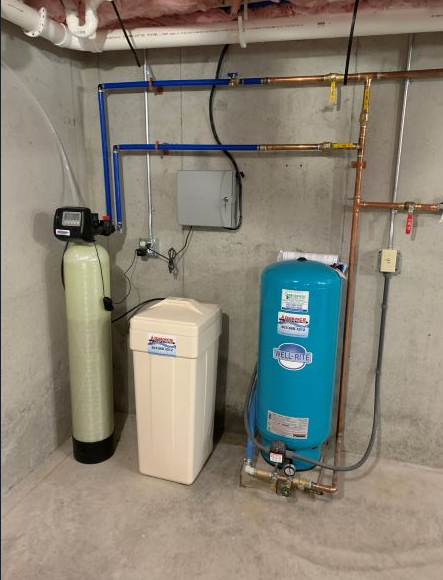
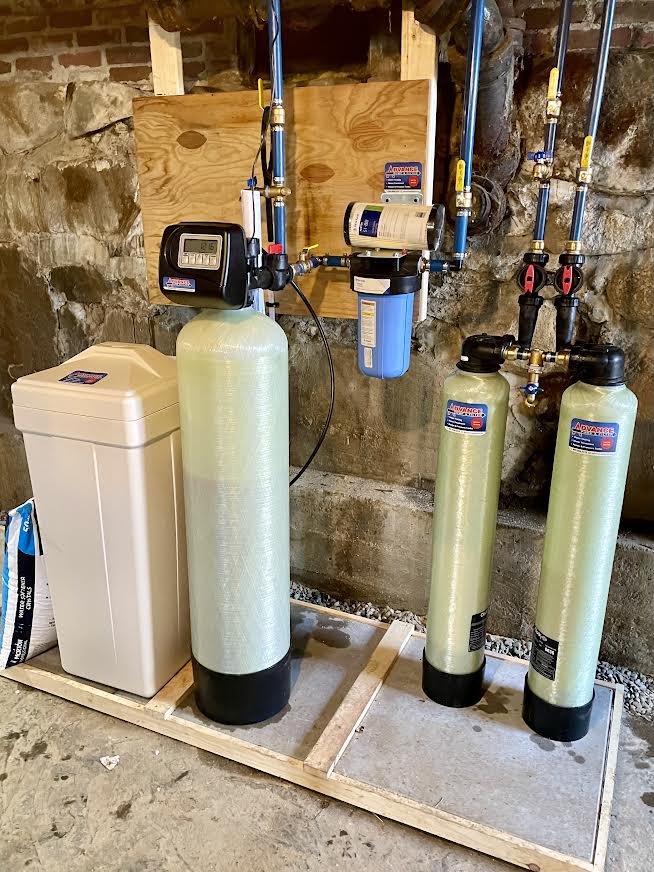



What are the benefits of having a water softener?
- Makes richer lather while bathing or showering
- Reduces the amount of soap and synthetic detergents used
- Prevents unsightly soap scum rings in the bathtub, stains and chalky deposits on hot and cold water fixtures
- Dishwashers, in areas having very hard water, can cut detergent use by more than 50 percent after softening [Water Quality Association (2011) Softened Water Benefits Study. Lisle: WQA]
- Reduces the build-up of scale deposits in all water-using appliances and hot water pipes
- Prevents hard-to-remove spots and streaks on glassware and dishes
- Prevents soap curd and detergent deposits on fabric
- Prevents dull colors and graying or yellowing of white fabrics
- In washing machines, can reduce detergent use by 50 percent and save energy by washing in 60ºF cold softened water instead of 100ºF hard hot water, achieving the same or better stain removal and whiter clothes compared to results in hard water.
How does a water softener work?
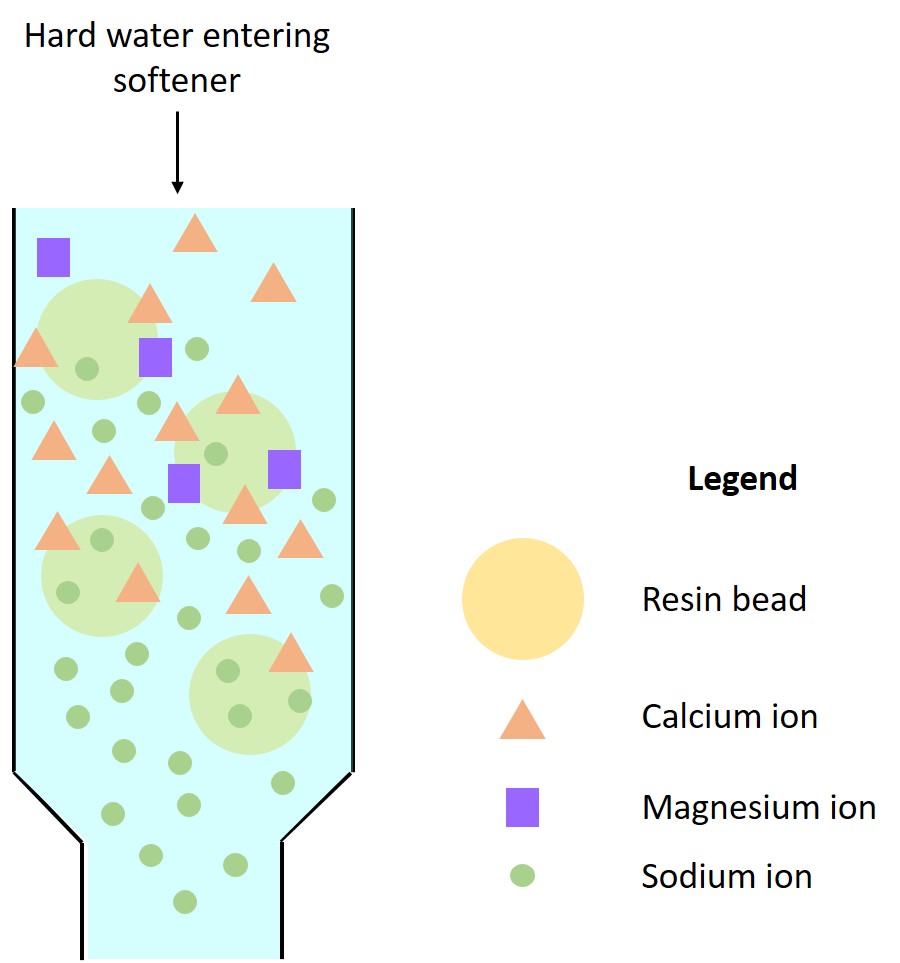
As water flows through the softener resin bed, and a process called ionic exchange occurs. The Resin beads come pre-charged with salt ions, and because the resin has a higher affinity for hardness ions than for salt ions, the resin will release the salt ions into the effluent water and will grab onto the hardness ions within close proximity. Over time the bed will reach a capacity where the resin is no longer able to remove hardness from the water. The softening system then needs to go through a regeneration cycle which will remove the hardness ions from the resin and will recharge the resin with salt ions. Softeners can either regenerate on a timed system, a gallon metered system, or a combination of the two. A full regeneration is accomplished through a series of cycles controlled by the softener valve and generally takes an hour and a half.

The regeneration cycles of a water softener:
Backwash #1– The control valve directs a high flow of water in the opposite direction of the normal flow of the softener. For a downflow water softener, the backwash sends water rushing from the bottom of the tank to the top. This evacuates any suspended solids to the drain line and loosens the resin bed.
Slow Brine Rinse– Control valve draws brine solution from the brine tank and permeates it through the resin bed. As this happens, salt ions overwhelm the resin beads and begin replacing the remaining hardness ions on the resin beads. .
Backwash #2– The system will then go through a 2nd backwash which flushes out the final remaining hardness molecules and a good portion of the brine solution.
Rapid Rinse– The control valve directs a large flow of water from the top of the tank to the bottom. This final rinse flushes out the rest of the brine solution and packs down the media bed before the system is put into service.
Brine Fill– The softening valve will direct water to refill the brine tank. This water will then mix with the salt in the brine tank which in a short period of time, will create a brine solution which will then be used for the next regeneration process.
A regeneration should occur when water is not being used. This is because the valve will bypass the system during a regeneration so any water being called to the house will be untreated. 2:00 am is a common time to schedule a regeneration because it is generally a time when no one is using water. Regardless, we can schedule the regeneration to meet your lifestyle needs.
How often should you be adding salt to the brine tank?
We generally find that softener owners will add a 40 lb – 50 lb bag of salt to the brine tank once per month.
The amount of salt your water softening system uses in any given month depends on the amount of hardness in your water, your water usage, and your system design. Regardless, we suggest checking your brine tank salt level once a month. Try to keep salt above the water level and try not to fill the brine tank over ¾ of the way full.
Basic Troubleshooting
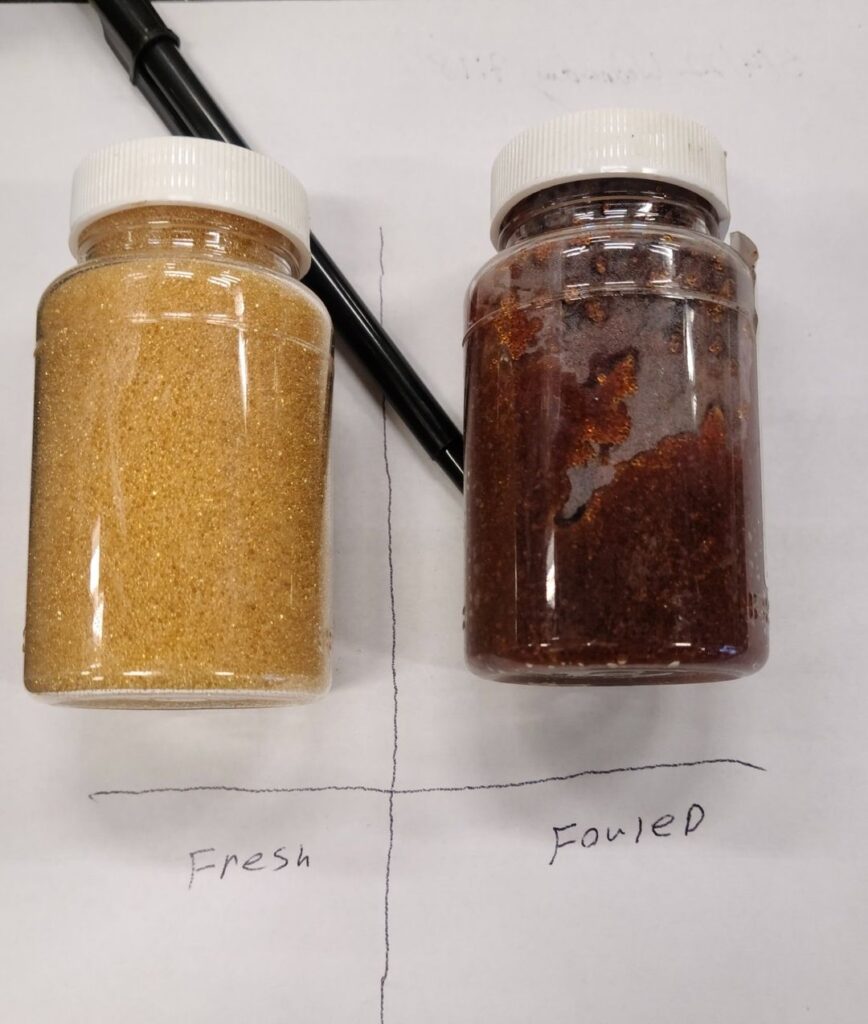
If you are are noticing that you are getting iron staining or hardness build up, you will want to check the following:
- Confirm that there is salt in the brine tank. Without a briney solution, the system cannot regenerate properly.
- Confirm that the time on the softener is correct. If the timer is not matching the current time of day, then your system may be regenerating when water is being used.
- See if there are any error codes on the softeners display screen (this is relevant for computerized systems.)
If everything seems to be in order, we will then need to schedule an onsite visit to determine if your raw water signature has changed or if there is a mechanical malfunction somewhere in your water treatment system.
Water softeners are one of the most common forms of water treatment in the United States. They are tried and true. It is a piece of water technology that a homeowner benefits from every time water is used in the home. A water softener can be a valuable investment because it can help to protect your appliances, improve the function of your home, and can save you money in the long run.
Every water source is different and may require different forms of treatment. We always recommend having an onsite evaluation and water test. If you have any questions about water softeners, or would like to schedule a no charge eval, please give us a call at 603-868-3212.


